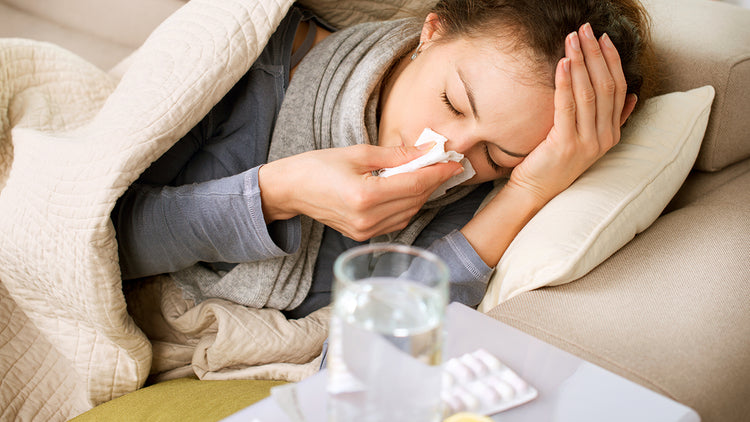
Strep throat is one of the most common upper respiratory tract bacterial infections. Strep throat is common among school-age kids, affecting nearly 30% of children visiting their healthcare facility with a sore throat.
The bacteria that causes strep throat is very susceptible to common antibiotics like penicillin which is why most doctors will prescribe a course of antibiotics to treat strep throat. However, although strep is common, most general sore throats are caused by viruses and will not need antibiotics. The only way to know for sure is by taking a rapid strep test which now can be done at home, or a throat culture to confirm if it’s actually a strep throat infection.
Strep throat is a relatively simple infection that can be treated quickly with antibiotics. It can also resolve itself without treatment in a matter of days. However, leaving it untreated to go away on its own can put you or your child at risk for some pretty serious complications.
Complications of Untreated Strep Throat
- Rheumatic fever: If strep throat goes undiagnosed, the bacterial infection can impact the immune system. This condition can lead to joint pain and affects the nervous system. It may give rise to diseases like arthritis, damage to heart valves, and potential heart failure in some cases.
- Kidney problems: Kidney problems following strep throat infection are more common and dangerous. Strep throat complications may include permanent kidney damage.
- Toxic Shock Syndrome: Untreated strep throat can lead to toxic shock syndrome leading to organ damage such as liver, lungs, or renal dysfunction, potentially life-threatening.
- Otitis media: Untreated strep throat can lead to infection in the middle ear-called Otitis media. It is more prominently found in infants, toddlers, and also adults. The bacteria may cause the ear tissue, including the eardrums, to become swollen. The bacteria can promote fluid build-up, making people dizzy and nauseous in some cases.
- Meningitis: Meningitis is another severe sign of strep throat infection. It can cause inflammation of the membrane surrounding the spinal and brain cords.
- Pneumonia: Untreated strep throat has also been found to cause Pneumonia. An infection of the lungs is characterized by inflammation in airspaces. This condition can turn fatal in 30%, making the recovery process difficult.
- Abscess: This severe complication is also one of the complications commonly noticed in strep throat infection. It can lead to pus-filled pockets forming near the tonsils.
Why Rheumatic Fever Can Life-Threatening
One complication of untreated strep is Acute Rheumatic fever (ARF). Acute Rheumatic fever is a life-threatening complication of a Strep throat infection. Strep throat is caused by a bacteria called Streptococcus pyogenes.
Acute Rheumatic fever occurs when the body’s immune system confuses the bacteria and the body’s cells, attacking the body. Rheumatic fever can develop into Rheumatic heart disease, which can leave permanent damage to the heart and cause heart attacks. According to recent studies, over 33 million Rheumatic heart disease cases are reported every year around the globe, leading to 275,000 deaths annually.
Rheumatic heart fever occurs after the onset of strep throat symptoms. It is characterized by a high-grade fever, severe joint pain and swelling, shortness of breath with difficulty breathing, behavioral and movement disturbances, and nodules on the skin.
Although Rheumatic heart fever can develop in anyone, this disease occurs mostly in specific high-risk groups. Children, people with repeated strep throat infections, individuals with weakened immune systems, and those living in areas dealing with overcrowding or poor sanitation are all at greater risk for Rheumatic heart fever. Household and school overcrowding is a major risk factor for acute rheumatic fever. Reduced overcrowding has been cited as one of the most important factors in the decline of acute Rheumatic fever.
The risk of Rheumatic heart fever is primarily seen in children 5-14 years old. It’s very rare in children under three and adults. Rheumatic heart fever is equally distributed among both males and females, but females are at twice the the risk of developing Rheumatic heart disease than males.
How to Prevent Rheumatic Heart Disease
The first step in preventing Rheumatic heart disease is preventing strep throat infections. Strep throat infection spreads easily through close contact. Reducing overcrowding in apartment buildings, schools, offices, and military facilities helps reduce the rate of Strep infection transmission.
But the most dramatic measure we can take against Rheumatic heart disease is quickly and accurately diagnosing a strep throat infection. With a quick diagnosis, antibiotics can be started immediately, and the risk of transmission reduces each day as the antibiotics work against the bacteria.
In order to diagnose strep throat, you must take a rapid strep test or throat culture. Strep throat is treated with antibiotics. You can get fast treatment by using Checkable's at-home strep tests and app to diagnose, treat, and get meds, all from home and in just minutes. Don't guess; test. It can be life-saving.
Life is too short to sit in a doctor’s office
Sign up for our weekly newsletter and get valuable healthcare tips and tricks in your inbox!
Sign up now and unsubscribe anytime.
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Press the space key then arrow keys to make a selection.