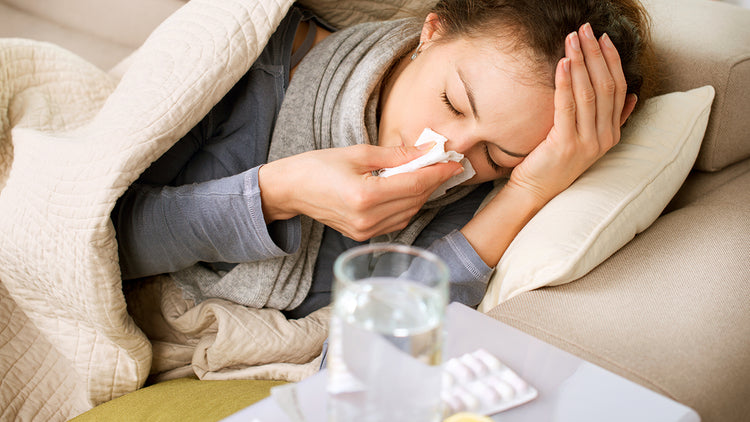
A sore throat is a common symptom of several viruses and can be especially prevalent during winter months. A sore throat is mostly caused by viruses such as the common cold, covid-19, or Epstein-Barr virus. However, it can also be caused by bacteria, and the most common among them is group A β-hemolytic streptococcus or in short (GAS), and in this case, it is known as strep throat.
It's important to distinguish between viral and bacterial causes of sore throat because treatments are different. Although viruses cause the majority of cases worldwide, a sore throat is less harmful and can resolve without any medication. On the other hand, strep throat, which accounts for a quarter of sore throat cases, can be more serious if left untreated. Strep throat can lead to lethal complications such as bacteremia, sepsis, or rheumatic heart disease.
Infectious Mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis, sometimes called Mono or the Kissing Disease, is a viral infection caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. It is estimated that it infects more than 90% of the adult population worldwide. However, only 66% of children get infected. Most infectious mononucleosis infections are asymptomatic. However, about a quarter of the infected people suffer from lymphadenopathy, which is an enlargement of lymph nodes, and sore throat symptoms. Infectious mononucleosis infection is generally self-limiting meaning that the infection can resolve spontaneously without any medication, however in rare occasions, it can cause fatal complications such as pancreatitis (serious inflammation of the pancreas), myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscles) and meningoencephalitis (inflammation in the brain).
Mono Vs. Strep Throat
Infectious mononucleosis and strep throat symptoms can be quite similar, and the distinction between these two infections is important. While infectious mononucleosis is primarily a self-limiting illness, strep throat is a bacterial infection that needs to be treated with oral antibiotics, or else dangerous complications can arise.
Despite the close similarities, the combination of symptoms may give clues on whether this is a strep throat infection or infectious mononucleosis. In addition to a sore throat, strep throat is characterized by headache, myalgia (muscular pain), malaise (general fatigue), white patches in the back of the throat, and fever. On the other hand, infectious mononucleosis may cause lymph node enlargement, extreme fatigue, and symptoms that last over two to four weeks.
Other than the symptoms, strep throat infection can be distinguished from infectious mononucleosis infections by using laboratory tests such as rapid antigen detection tests or in short (RADTs) for strep throat, which can give results rapidly within 10 minutes. In case there is no RADT or any other testing measures, researchers have developed an index to make a distinction between strep throat and infectious mononucleosis.
This index is called the infection discrimination index (IDI), and it's based on a simple blood test called Complete Blood Count (CBC). The basis of this index is dependent on the fact that the number of certain types of immune system cells increase in strep throat, while others increase in infectious mononucleosis. The scientists concluded that this index could contribute to the distinction between strep throat and infectious mononucleosis due to its accuracy, practicality, safety, and cost-effectiveness. However, if resources were available RADTs remain a faster and less invasive method to distinguish between infectious mononucleosis throat and strep throat. And now, with Checkable's at-home strep tests, you can get answers in minutes and start feeling better.
Life is too short to sit in a doctor’s office
Sign up for our weekly newsletter and get valuable healthcare tips and tricks in your inbox!
Sign up now and unsubscribe anytime.
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Press the space key then arrow keys to make a selection.